Market Potential for Reclaiming CCA from Decommissioned Utility Poles
Natural Wood Durability
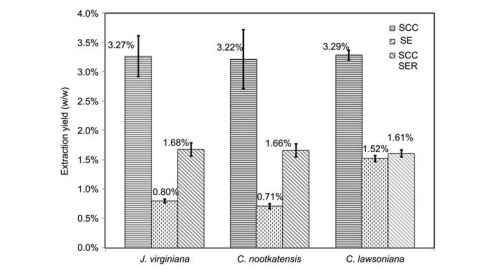
The relationship between chemical composition and durability in wood was first reported by Hawley et al. (1924). Some heartwood has the inherent ability to resist biological degradation, often referred to as ‘‘natural durability’’ or ‘‘decay resistance’’ (Eaton and Hale 1993). Meanwhile, the relation between extractive content of heartwoods and their fungal tolerance is well established (see recent publications: Chedgy et al. 2007; Lim et al. 2007; Mburu et al. 2007; Kusuma and Tachibana 2008). Three North American important commercial wood species, Port-Orford cedar (Chamaecyparis lawsoniana), Alaska yellow cedar (Chamaecyparis nootkatensis), and Eastern red cedar (Juniperus virginiana) are known to have significant natural durability. Cedar species have been reported to have special bioactivity against termites and wood decay fungi (Liu 2004; Gao et al. 2008). Evaluations on antifungal properties (Gao et al. 2008), biocidal application (Dolan et al. 2007), and termiticidal activities (Liu 2004) of C. lawsoniana extracts have been reported. A chemical ecological study of the components of the essential oil of J. virginiana from different habitats was performed by Setzer et al. (1992). Volatile oil from J. virginiana, consisting primarily of cedrene (a terpene) and cedral has been used in perfumery (Heide et al. 1988; Semen and Hiziroglu 2005) and as an insect repellent. J. virginiana oil has been widely used in a very broad range of products owing to its unique properties, such as odor and repellency or toxicity to many pests.
Antibiotic Activity of Cedar Extractives
To read more please visit our publication: Antifungal activities of three supercritical fluid extracted cedar oils
Meet the Author
Dr. Todd Shupe is the President of Wood Science Consulting, LLC. He is a well-recognized expert on wood forensics, wood preservation, wood decay and degradation, and wood species identification. He has a broad background in new product development, quality management, and marketing and sales in both the public and private sectors. For more information please visit DrToddShupe.com.
We welcome your comments below.
Thank you for visiting. We trust that you have enjoyed reading our articles.
Liked this post? Read more below or search for more topics . . .